Metric Threads
Metric Thread Note Components
After drawing a thread, we need to identify the size and thread form in a thread note.
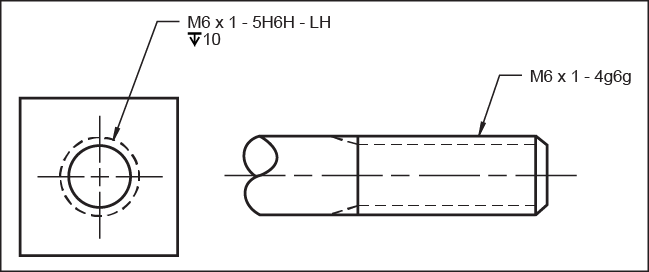
The following items are included in a thread note.
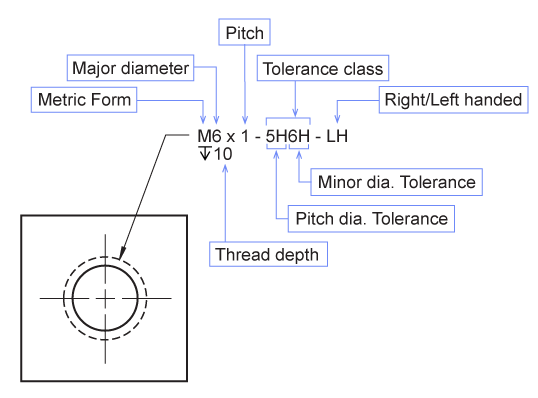
- Metric Form: Placing an M before the major diameter indicates the metric thread form.
- Major Diameter: The largest diameter.
- Pitch: (P) Millimeters per thread.
- Tolerance Class: It describes the looseness or tightness of fit between the internal and external threads. Two classes of metric thread fits are generally used.
- 6H/6g = General purpose. A tolerance class of 6H/6g is assumed if it is not specified.
- 6H/5g6g = Closer fit.
- Tolerance Grade: (Number) Smaller numbers indicate a tighter fit.
- Tolerance Position: (Letter) Specifies the amount of allowance.
- Upper case letters = internal threads
- Lower case letters = external threads
- Right handed or Left handed Thread:
- RH = Right handed (right handed threads are assumed if not stated.)
- LH = Left handed
- Depth of thread: The thread depth is given at the end of the thread note and indicates the thread depth for internal threads. This is not the tap drill depth.
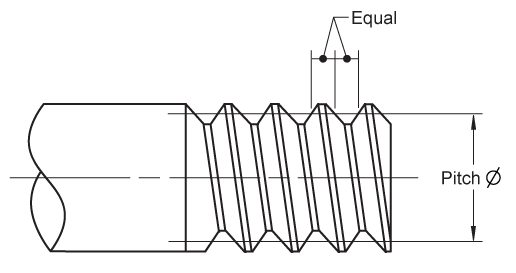
What is the pitch diameter?
The metric thread note may contain a pitch diameter tolerance. The pitch diameter cuts the threads at a point where the distance of the spaces equal the distance of the threads.